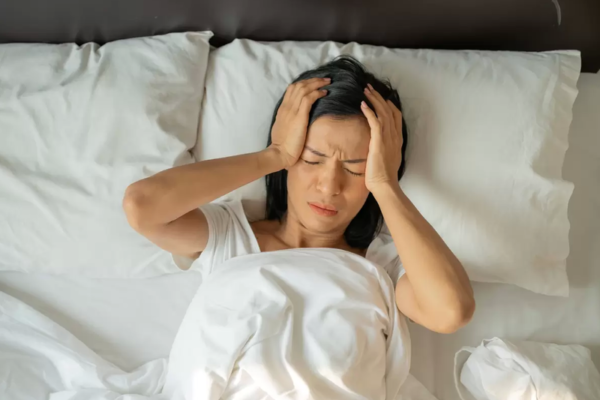
Migraines are a type of excruciating headache that make you so unwell you can’t function normally when you’re having an attack. If you get migraines and dread the next one, Dr. Andrews, MD, board-certified interventional pain specialist at No Pain, can offer some effective treatments that could make your life much easier. Dr. Andrews is a leading expert in headaches and other forms of chronic pain. If migraines affect your life, call today to schedule a consultation or book an appointment online.
Migraine
Migraine Q & A
What is a migraine?
A migraine is a type of headache that causes severe head pain along with a collection of other unpleasant symptoms, including:
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Blurred vision
- Lightheadedness
- Sensitivity to light, sound, touch, and smell
Migraine headaches are usually debilitating, with patients being forced to stay still and quiet while the migraine runs its course. Most people who experience migraines do so regularly, some very frequently, others on rare occasions, but they usually learn to notice the signs that a migraine is coming.
The signs you experience are unique to you, but could include mood swings, digestive problems, or disturbed sleep. Some people who get migraines have visual and sensory disturbances called auras, which can look like flashing lights or spots in front of your eyes. Auras can also affect your speech and sense of touch.
What causes a migraine?
The exact reason why some people experience migraines and others don’t isn’t clear. Most people have headaches now and again, but far fewer experience migraines. What doctors do know is that the trigeminal nerve in your head is the source of migraine symptoms, and that very often there are triggers that can lead to a migraine attack, such as:
- Estrogen-based medication (birth control or HRT pills)
- Stress
- Bright lights
- Sun glare
- Strong odors
- Getting too much or too little sleep
- Intense physical activity
- Changes in the weather
Diet is a common factor in triggering migraines. Eating processed foods, highly salted foods or aged cheeses, and food additives like aspartame and monosodium glutamate can trigger migraines. So can alcohol and eating irregularly or fasting.
What treatments are available for migraines?
Treatments for migraines primarily consist of medications that prevent a migraine from starting, stop it getting worse, or reduce the number of migraines you get. Possible medications that Dr. Andrews recommend include:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- Triptans
- Ergotamine and caffeine
- Anti-nausea medicine
- Glucocorticoids
- Beta-blockers
- Calcium channel blockers
- Lisinopril (angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor)
- Tricyclic antidepressants
- Anti-seizure drugs
- Steroid trigger point injections
Medical Botox® injections are also effective in relieving migraine pain for patients who find other types of treatments don’t help.
If you regularly have migraines, call No Pain today or book an appointment online.
WHAT WE OFFER
Chronic Pain Conditions and Treatments
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Migraine
Coming Soon. Learn More.
Did you know that?
Donec sed odio dui. Nulla vitae elit libero, a pharetra augue. Nullam id dolor id nibh ultricies vehicula ut id elit. Integer posuere erat a ante venenatis dapibus posuere velit aliquet.
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-