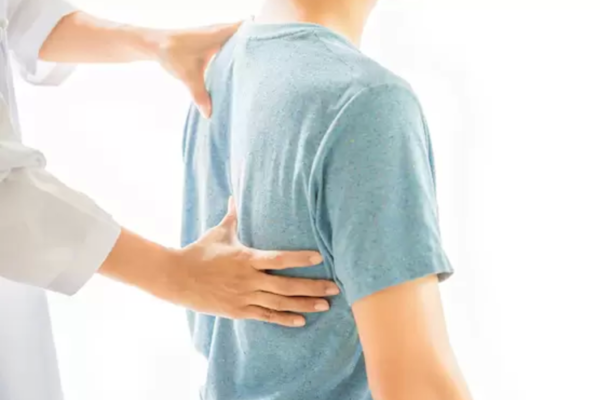
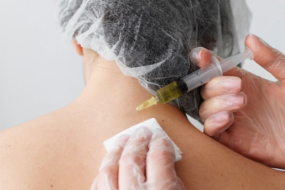
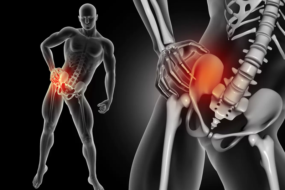
Back pain affects most people at some point and usually clears up within a few weeks. But for millions of Americans, it becomes a chronic problem that takes over their lives. If you have back pain, Dr. Andrews, MD, board-certified interventional pain specialist at No Pain, can help. Dr. Andrews is a leading expert in chronic pain and spinal conditions. If back pain affects your quality of life, call today to schedule a consultation or book an appointment online.
Back Pain
Back Pain Q & A
What causes back pain?
Back pain could be the result of an acute injury or develop because of tissue degeneration from wear and tear over the years. In some cases, untreated acute back injuries turn into chronic pain problems. In others, tissue degeneration leads to an acute attack of pain.
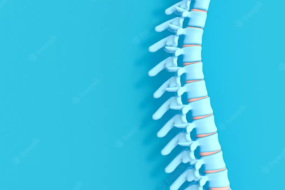
Your spinal column is made up of vertebrae that each have a small joint, with spinal discs that sit between each vertebra to act as a shock absorber. Supporting and stabilizing the vertebrae are the ligaments and muscles, and inside the spinal column is your spinal cord, which, together with your brain, makes up your central nervous system. The spinal cord is like a hub for your peripheral nerves, which spread out into your body from their roots in the spinal canal.
One or more of these structures can be a source of pain when they get worn or sustain damage. In addition to the pain, you might experience other symptoms, such as loss of function in your legs and numbness, tingling, prickling, or burning sensations.
What conditions might give me back pain?
Most back pain relates to your musculoskeletal system, your bones, ligaments, tendons, cartilage, and muscles. The most common back conditions include:
- Damaged ligaments
- Pulled muscles
- Osteoporosis
- Arthritis
- Sciatica
- Degenerative disc disease
- Herniated discs
- Spinal stenosis (narrowing of the spine)
- Osteophytes (bone spurs)
In some occasions, back pain is a symptom of an internal problem, such as a kidney infection. It’s important to know for sure why your back hurts so you can get the right treatment.
How is back pain treated?
Dr. Andrews first needs to diagnose the cause of your back pain. He reviews your medical history and current symptoms, and performs a physical exam. You may also need to undergo diagnostic imaging tests such as X-rays, MRI scans, or CT scans to confirm a suspected diagnosis and assess the problem in more detail.
Once Dr. Andrews makes his diagnosis, he creates a treatment plan that contains the therapeutic approaches most likely to result in pain relief. Initial treatments are likely to include physical therapies to aid healing of the damaged tissues and keep you strong and flexible, rest, and medication to relieve pain and reduce inflammation.
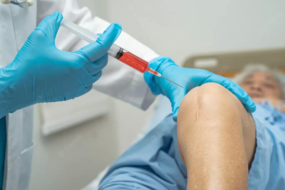
If your pain is bad or you’re finding it hard to stay active, an epidural steroid injection into your back can give you temporary relief. You may also have a condition for which regenerative medicine techniques could help accelerate and boost new tissue growth.
Surgical options
If these initial approaches don’t work or your pain is unlikely to resolve on its own, you may need to consider surgical options such as:
- Partial vertebra elimination
- Discectomy or microdiscectomy
- Artificial disc implantation
- Facetectomy
- Foraminotomy
- Laminectomy or laminotomy
- Spinal fusion
- Spinal cord or dorsal root ganglion stimulation
For the most effective treatment of back pain, call No Pain today or book an appointment online.
WHAT WE OFFER
Chronic Pain Conditions and Treatments
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Migraine
Coming Soon. Learn More.
Did you know that?
Donec sed odio dui. Nulla vitae elit libero, a pharetra augue. Nullam id dolor id nibh ultricies vehicula ut id elit. Integer posuere erat a ante venenatis dapibus posuere velit aliquet.
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-