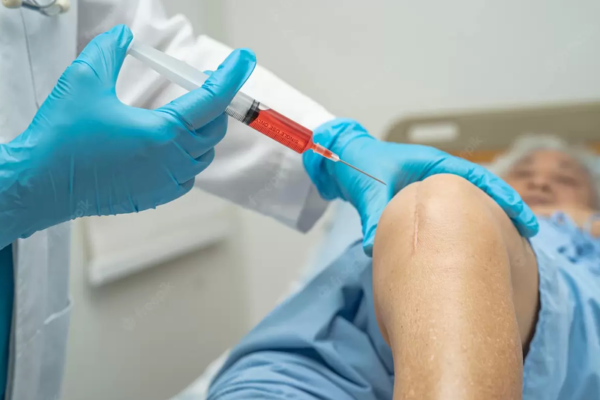
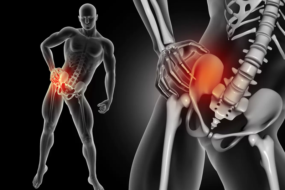
Knees are joints that take a great deal of strain day in and day out, and sometimes something has to give. If you have pain in your knees, it could be an injury that can’t heal properly without treatment, or a degenerative condition, both of which Dr. Andrews, MD, board-certified interventional pain specialist at No Pain, can successfully treat. Dr. Andrews is a leading expert in chronic pain. If your knees won’t stop hurting, call the practice today to schedule a consultation or book an appointment online.
Knee Pain
Knee Pain Q & A
What causes knee pain?
Knee pain is a frequent problem, especially for athletes and people who lead physically active lives or do a lot of kneeling. Knees support most of your body weight when you’re standing and moving about, and have to twist, turn, and absorb considerable impact shock to enable you to carry out your normal daily activities.
Inside your knee are the ends of your thigh bone and shin bone that form the main joint. These bones sit within a network of tendons, ligaments, and muscles, as well as nerves, blood vessels, and cartilage. Any of the structures or tissues in your knee can sustain an injury from overuse or trauma, or degenerate over time.
What conditions affect the knees?
Knee pain may be traumatic or degenerative, or have elements of both. Conditions that cause knee pain include:
- Fractured bones
- Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) tear
- Medial collateral ligament (MCL) tear
- Meniscus tear
- Patellofemoral syndrome
- Patellar tendinitis (runner’s knee)
- Articular cartilage injuries
- Patellar (kneecap) instability
- Patellar dislocation
- Knee dislocation
- Iliotibial (IT) band injury
- Arthritis
ACL tears and damage to the meniscus inside the knee joint are injuries Dr. Andrews sees most often, especially in people who play sports.
How is knee pain diagnosed?
After reviewing your medical history and discussing your symptoms with you, Dr. Andrews examines your knee, checking for restrictions in your movement and feeling for any obvious signs of damage. You may also need to undergo diagnostic imaging tests to help with diagnosis and assess the extent of any tissue damage.
You might have an X-ray to check the bones in your knee, an ultrasound to check the muscles, ligaments, and tendons, or an MRI to check both hard and soft tissues.
How is knee pain treated?
Treatment for knee pain starts with conservative approaches in most cases, such as:
- Modifying your activity to take the stress off the injury
- Knee braces to provide support and reduce pressure
- Steroid injections into the joint
- Joint fluid replacement
- Physical therapy to rebuild strength and keep the knee flexible
- Regenerative medicine
Some injuries, such as certain ligament tears, can’t heal without treatment to repair the tissues. In these cases, or if your knee pain doesn’t respond to more conservative options, Dr. Andrews might suggest surgery.
Ligament repairs can be done in many cases using minimally invasive arthroscopic techniques, or you may need a partial or total knee replacement.
Find out more about the treatments available to ease your knee pain by calling No Pain today or booking an appointment online.
WHAT WE OFFER
Chronic Pain Conditions and Treatments
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Migraine
Coming Soon. Learn More.
Did you know that?
Donec sed odio dui. Nulla vitae elit libero, a pharetra augue. Nullam id dolor id nibh ultricies vehicula ut id elit. Integer posuere erat a ante venenatis dapibus posuere velit aliquet.
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-